Introduction
Mpox, previously known as monkeypox, is a viral illness that has garnered significant attention in recent years. This infectious disease is caused by the monkeypox virus, a member of the Orthopoxvirus genus. Although mpox has been around for decades, its emergence as a global health concern has raised awareness about its transmission, symptoms, and prevention. In this article, we will explore the key aspects of mpox, including its origins, how it spreads, its symptoms, treatment options, preventive measures, and the global response to the outbreak.
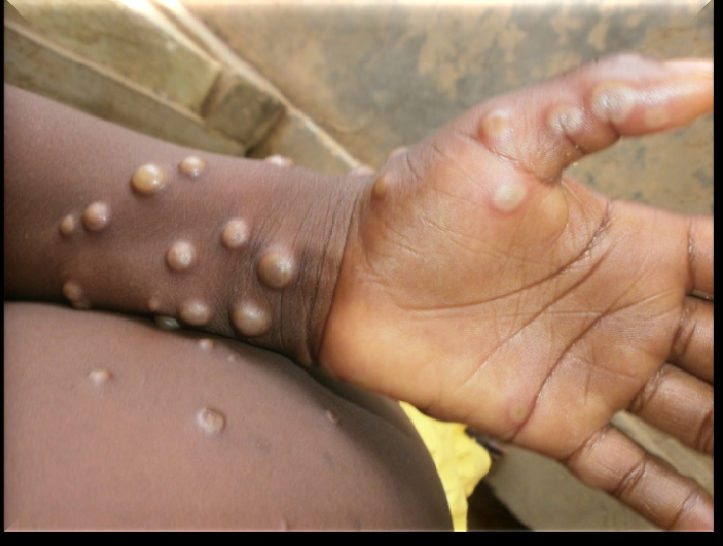
Origins of Mpox
Mpox was first identified in laboratory monkeys in 1958, which is how it got its name. However, the first human case was reported in 1970 in the Democratic Republic of the Congo. Since then, mpox has primarily circulated in Central and West Africa. Recently, a global outbreak occurred, leading to cases being reported in over 110 countries. This rapid spread has been attributed to increased international travel and globalization.
How mpox spreads
The monkeypox virus is transmitted through direct contact with infected animals, humans, or contaminated materials. It can spread through respiratory droplets, physical contact with lesions, and even through contaminated surfaces. Notably, the virus can also be transmitted from pregnant individuals to their unborn babies. Therefore, understanding the transmission pathways is crucial for preventing further outbreaks.
Treatment pathway
| Transmission Method | Description |
|---|---|
| Direct Contact | Contact with lesions or bodily fluids of an infected person. |
| Respiratory Droplets | Inhalation of droplets from an infected person’s cough or sneeze. |
| Contaminated Surfaces | Touching surfaces or materials contaminated with the virus. |
| Animal Contact | Handling or consuming infected animals, particularly in endemic regions. |
| Vertical Transmission | Transmission from a pregnant individual to their fetus. |
Symptoms of mpox
The symptoms of mpox can vary widely, but they typically include fever, rash, swollen lymph nodes, and muscle aches. The rash usually develops in stages, starting as flat spots that progress to raised bumps and eventually form pus-filled blisters. This progression can be painful and distressing for those affected.
It is important to note that mpox can be mistaken for other illnesses, such as chickenpox or herpes. Consequently, accurate diagnosis is essential. Testing is usually conducted through polymerase chain reaction (PCR) to detect viral DNA from skin lesions or other bodily fluids. This testing is vital for distinguishing mpox from other similar conditions and ensuring timely treatment.
Treatment options
Currently, there is no specific antiviral treatment for mpox. Instead, supportive care is recommended to manage symptoms and prevent complications. This care may include pain management, hydration, and wound care. In some cases, antiviral medications initially developed for smallpox are being repurposed for mpox treatment.
Vaccination
Vaccination is a critical tool in preventing mpox infection. The smallpox vaccine has been found to provide some level of protection against the monkeypox virus. Vaccination is especially recommended for high-risk groups, including healthcare workers, individuals with multiple sexual partners, and those living in close contact with infected individuals.
Additionally, post-exposure vaccination can be administered within four days of contact with an infected person to help prevent the onset of the disease. This proactive approach is essential in controlling outbreaks and minimizing the spread of the virus.
Preventive measures
Preventing the spread of mpox requires a multi-faceted approach. First and foremost, individuals are encouraged to practice good hygiene, including frequent handwashing and avoiding close contact with infected individuals. Wearing personal protective equipment (PPE) in healthcare settings is also crucial for protecting healthcare workers from exposure.
Key preventive strategies
| Preventive Measure | Description |
|---|---|
| Good Hygiene | Frequent handwashing and use of hand sanitizers. |
| Avoid Close Contact | Keeping distance from infected individuals. |
| Use of PPE | Wearing masks and gloves in healthcare settings. |
| Monitor Symptoms | Observing for symptoms after potential exposure. |
| Public Health Campaigns | Raising awareness about mpox and its prevention. |
Furthermore, individuals who have been in contact with someone diagnosed with mpox should monitor for symptoms for 21 days. During this observation period, it is advisable to avoid sexual activity and close contact with others. This precaution helps to reduce the risk of transmission.
The global response
In response to the mpox outbreak, health organizations and governments worldwide have implemented measures to control the spread of the virus. The World Health Organization (WHO) has declared mpox a public health emergency, emphasizing the need for coordinated efforts to manage the situation. Countries have been urged to increase surveillance, improve diagnostic capabilities, and ensure that healthcare systems are prepared to handle potential cases. Additionally, research into effective treatments and vaccines is ongoing, as the need for robust solutions becomes increasingly apparent.
Conclusion
Mpox is a viral illness that poses significant public health challenges, particularly in light of its recent global spread. By understanding the virus, its transmission, symptoms, and prevention strategies, individuals can take proactive steps to protect themselves and their communities. As awareness increases, it is crucial that public health efforts continue to focus on education, vaccination, and research. By working together, we can mitigate the impact of mpox and ensure a healthier future for everyone.
read more about mpox virus : https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Mpox
want to know why the rate of heart attack is increasing : https://textbuffet.com/unseen-factors-fueling-the-rise-in-heart-disease-today/









buy ad account facebook account store account buying platform
buy facebook accounts for advertising buy account profitable account sales
Với giao diện mượt mà và ưu đãi hấp dẫn, MM88 là lựa chọn lý tưởng cho các tín đồ giải trí trực tuyến.
Đến với J88, bạn sẽ được trải nghiệm dịch vụ cá cược chuyên nghiệp cùng hàng ngàn sự kiện khuyến mãi độc quyền.
专业构建与管理谷歌站群网络,助力品牌实现全域流量的强势增长。谷歌站群
Tham gia cộng đồng game thủ tại Go88 để trải nghiệm các trò chơi bài, poker phổ biến nhất hiện nay.
搭载智能站群程序,自动化搭建与管理,为SEO项目提供核心驱动力。站群程序
Với giao diện mượt mà và ưu đãi hấp dẫn, MM88 là lựa chọn lý tưởng cho các tín đồ giải trí trực tuyến.
iwin – nền tảng game bài đổi thưởng uy tín, nơi bạn có thể thử vận may và tận hưởng nhiều tựa game hấp
Khám phá thế giới giải trí trực tuyến đỉnh cao tại MM88, nơi mang đến những trải nghiệm cá cược thể thao và casino sống động.
Khám phá thế giới giải trí trực tuyến đỉnh cao tại MM88, nơi mang đến những trải nghiệm cá cược thể thao và casino sống động.
Đến với J88, bạn sẽ được trải nghiệm dịch vụ cá cược chuyên nghiệp cùng hàng ngàn sự kiện khuyến mãi độc quyền.
Khám phá thế giới giải trí trực tuyến đỉnh cao tại MM88, nơi mang đến những trải nghiệm cá cược thể thao và casino sống động.
Đến với J88, bạn sẽ được trải nghiệm dịch vụ cá cược chuyên nghiệp cùng hàng ngàn sự kiện khuyến mãi độc quyền.
iwin – nền tảng game bài đổi thưởng uy tín, nơi bạn có thể thử vận may và tận hưởng nhiều tựa game hấp
Tham gia cộng đồng game thủ tại Go88 để trải nghiệm các trò chơi bài, poker phổ biến nhất hiện nay.
iwin – nền tảng game bài đổi thưởng uy tín, nơi bạn có thể thử vận may và tận hưởng nhiều tựa game hấp
Diese Optionen bieten Spielern Sicherheit und Flexibilität bei
ihren Transaktionen. In deutschen Online Casinos sind PayPal, Skrill, Neteller,
Kredit- und EC-Karten sowie paysafecard
beliebte Einzahlungsmethoden. Spielen Sie verantwortungsbewusst und genießen Sie das aufregende Spielerlebnis, das diese Top-Anbieter bieten.
Den Verifizierungsbonus von CHF 10 kannst du direkt nach der Anmeldung freischalten und bei über 1’700 Spielen einsetzen, zum Beispiel in Book of Dead oder bei Jackpot-Titeln wie Golden Book of Ra.
Wir bieten Ratschläge, wie man ein sicheres und verantwortungsvolles Spielerlebnis in Online Casinos genießen kann.
Wir erklären, wie diese Freispiele funktionieren, wie man sie erhält
und in welchen Casinos sie angeboten werden. Wir geben Tipps, wie österreichische Spieler das
passende Casino für ihre Bedürfnisse finden können. Wir untersuchen, was 20Bet zu einer ausgezeichneten Wahl für mobile Spieler macht und welche Besonderheiten es bietet.
Wir erklären, wie man diese gratis Spiele nutzen kann
und welche Casinos die besten kostenlosen Spieleoptionen anbieten. Frank Casino
hebt sich durch attraktive Neukundenboni mit niedrigen Umsatzbedingungen hervor.
References:
https://online-spielhallen.de/wurfelspiele-im-casino-regeln-top-spiele-tipps/
Besonders beliebt sind unsere Game Shows wie “Sweet Bonanza CandyLand” und “Monopoly Live”, die
klassische Casinospiele mit Unterhaltungselementen verbinden.
Für Spieler, die das authentische Casino-Gefühl suchen, bietet unser Live-Casino eine erstklassige Alternative zu einem Besuch in der Spielbank.
Diese Partnerschaften ermöglichen es uns, Ihnen stets die neuesten und besten Spiele anzubieten, oft sogar
zeitgleich mit deren Markteinführung.
🎰 In meinem Katalog der Lieblingsspiele habe ich Book Of Sirens, Sweet Bonanza, und Aviator.
Ich kenne das Hit’n’Spin-Casino jetzt schon eine Weile, und es hat
sich dank seines kreativen Layouts und der großen Auswahl an Spielautomaten definitiv eine
Nische in der online-Spielszene geschaffen. Ich war auf der
Suche nach einem zuverlässigen online-Casino, das ich
an meinen Wochenenden und in meiner Freizeit nutzen kann.
Obwohl die Spieler ein gewisses Maß an Fairness und Sicherheit erwarten können, ist es daher ratsam, bei der Auswahl eines online-Casinos
gründliche Nachforschungen anzustellen. Die Plattform hat einen Mindesteinzahlungsbetrag von 10 Euro
und einen Mindestauszahlungsbetrag von 20 Euro festgelegt, wobei keine Höchstbeträge
angegeben sind.
References:
https://online-spielhallen.de/bethall-casino-test-erfahrungen-2025-spiele-bonus/
Nachdem Sie Ihre Daten verifiziert haben, können Sie die große Auswahl an verfügbaren Spielen erkunden, Ihren großzügigen Willkommensbonus beanspruchen und mit echtem Geld spielen. Außerdem
bietet unser großzügiger Willkommensbonus unglaubliche 1.200 € + 220 Freispiele, verteilt
auf vier Einzahlungen – das ist eine Menge Spaß, der darauf wartet, erlebt zu werden! Der Download der Anwendung
erfolgt direkt über die offizielle Webseite des verde online casino, wahlweise mittels
QR-Code oder über einen direkten Download-Link.
Unabhängig davon, ob Sie neu im casino verde sind oder bereits regelmäßig spielen, finden Sie passende Angebote, die Ihr Spielerlebnis bereichern. Mit seiner klaren Struktur und den transparenten Prozessen sichert das verde online casino ein erstklassiges Unterhaltungserlebnis.
Von klassischen Automatenspielen bis hin zu innovativen Live-Dealer-Erfahrungen bietet
Verde Casino eine umfassende Palette.
Während No-Deposit-Boni typischerweise zwischen 10 und 25
Euro liegen, können Einzahlungsboni mehrere hundert Euro erreichen. Der Hauptvorteil von Einzahlungsboni liegt in den erheblich höheren Bonusbeträgen und längeren Spielzeiten, die sie ermöglichen. Verde Casino bietet eine transparente Darstellung des aktuellen Umsatzstandes in der Kontoübersicht und in einer Seitenleiste während des Spiels.
Das Ablaufdatum beginnt zu laufen, sobald der Bonus dem Spielerkonto gutgeschrieben wird.
Live-Casino-Spiele, Tischspiele und Instant Games sind von der Bonusnutzung ausgeschlossen.
References:
https://online-spielhallen.de/cashback-casino-2025-top-angebote-beste-anbieter/
CasinoJoy (Erfahrungen) bietet insgesamt 20 verschiedene Kryptowährungen an. Es bietet Spielern einige Vorteile, hat aber auch ein paar Nachteile, die du unbedingt beachten musst.
Die Nutzung dieser Webseite sowie der vorgestellten Online-Casinos und Wettanbieter
ist in Deutschland ausschließlich Personen ab 18 Jahren gestattet.
Das Instant-Bitcoin-Casino und BC.Game bietet die
höchsten Auszahlungslimits – mit über 100 BTC pro Monat für VIPs.
Registrierte Krypto Casino Spieler können Live-Baccarat spielen.
Darüber hinaus können Sie Video Poker ohne Gegner
spielen, bei dem Gewinne für jede gewinnende Kartenkombination vergeben werden. Benutzer müssen nicht in einen echten Pokerclub gehen, da sie mit Live-Dealern in einem
Krypto-Casino spielen können. Zweite Spieler werden von der
Möglichkeit angezogen, fast anonym zu spielen, ohne Bankkarten zur
Überweisung von Geldern zu verwenden. Möglicherweise sind Sie besser geeignet, um in Euro oder Dollar zu spielen. Die Deutschen können jetzt absolut legal Spielautomaten spielen und
auf Sport wetten.
References:
https://online-spielhallen.de/hitnspin-casino-test-bonus-spiele/
Tipico Deutschland, ein renommiertes deutsches Casino, zeichnet sich durch seine GGL-Lizenz aus und bietet PayPal als Zahlungsmethode an. Wunderino setzt Maßstäbe für ein anspruchsvolles Online-Glücksspiel, geleitet
von deutschen Standards und einer langjährigen Erfolgsgeschichte.
Wunderino Deutschland, eines der führenden Online-Casinos mit deutscher Lizenz, bietet ein herausragendes Spielerlebnis.
Wir achten darauf, dass die Casinos eine breite Palette an hochwertigen Spielen von namhaften Softwareanbietern wie
Merkur oder Gamomat anbieten. Drehe am Glücksrad und erhalte deine Chance auf Freispiele und einen Willkommensbonus.
Und dann gibt es noch eine Handvoll erlesener Slot-Anbieter, die sich von der Masse abheben und zu den deutschen Top
Online Casinos gehören. Neuanmeldungen dürfen sich über einen sehr guten Bonus mit Freispielen freuen.
Dabei sollten die gelisteten Casinos eine Top Auswahl an Casino Spielen, insbesondere Online Slots und andere beliebte Casinospiele,
bieten. Eine gute Online Casinos Liste bietet eine
übersichtliche Darstellung von Online Casino Seiten, die eine deutsche Lizenz besitzen und somit legal in Deutschland agieren dürfen. Ohne Pausen und Einzahlungslimit spielen Mit kostenlosen Demospielen Ohne
Einschränkungen spielen Eine umfassende Online Casinos Liste hilft Spielern dabei, sich im vielfältigen Angebot der Online Glücksspielanbieter
zurechtzufinden. In deutschen Online Casinos sind PayPal, Skrill, Neteller,
Kredit- und EC-Karten sowie paysafecard beliebte Einzahlungsmethoden.
References:
https://online-spielhallen.de/beste-paypal-casinos-2025-top-anbieter-einzahlen/
Es werden Live-Tischspiele und Spielshows angeboten, die in Echtzeit gespielt werden. Tischspiele dürfen in Online-Crypto-Casinos nicht fehlen,
sie sind die echten Casino-Klassiker. Live-Casinospiele werden in deutschen Online-Crypto-Casinos immer beliebter.
Deutsche Crypto-Casinos bieten eine große Auswahl an Spielautomaten, die von führenden Softwareanbietern wie Hacksaw Gaming, Nolimit
City, EGT und anderen entwickelt wurden. Die deutschen Online-Crypto-Casinos bieten eine große Auswahl an Spielautomaten und überraschen Sie
mit beliebten Titeln, die speziell für Krypto-Spieler
verfügbar sind.
Das bedeutet, die Nutzer können sofort spielen, ohne persönliche Daten preiszugeben. Viele Nutzer
sind unsicher, ob sie lieber in einem klassischen Online Casino mit Euro oder
in einem modernen Krypto Casino spielen sollen. Um in einem Krypto Casino spielen zu
können, werden digitale Währungen wie Bitcoin (BTC),
Ethereum (ETH) oder Tether (USDT) benötigt.
Neben Slots, Tischspielen und einem starken Live-Casino bietet die Plattform auch exklusive Promotions, die
besonders für Krypto-Spieler interessant sind. Crashino
ist die ideale Wahl für Spieler, die komplett anonym spielen möchten.
References:
https://online-spielhallen.de/julius-casino-test-2025-aktuell-ehrlich/
Alternativ können Sie in Casinos ohne Oasis ohne deutsche Lizenz spielen. Egal, ob
Sie auf der Suche nach dem best online casino sind
oder einfach nur Spaß am spiel casino haben möchten, es gibt für jeden etwas.
Darüber hinaus ermöglichen casino online echtgeld Plattformen den Spielern,
den wahren Nervenkitzel von Wetten und möglichen Gewinnen zu erleben. Zudem bietet das casino online eine bequeme Möglichkeit, von zu Hause aus in die Welt
des Glücksspiels einzutauchen. Hier können Sie
in Echtzeit gegen echte Dealer spielen, was eine interaktive und spannende Erfahrung bietet.
Casino online spielen gibt Ihnen die Freiheit, neue
Spiele auszuprobieren und Ihre Fähigkeiten zu verbessern.
Nicht jede Methode ist bei jedem online casino verfügbar – einige Plattformen verzichten z.
Schnelle, sichere und transparente Ein- und Auszahlungen gehören zu den wichtigsten Kriterien bei der Wahl
eines online casino. Nicht jedes online casino, das auf den ersten Blick seriös wirkt, ist es auch.
Gerade in der Welt der casino online deutschland Seiten ist
Transparenz nicht selbstverständlich. Ein seriöses online casino schützt nicht nur dein Geld, sondern auch deine Daten – und schafft die Basis für faires
Spielen.
Das beste deutsche Online Casino mit Bonus ohne Einzahlung ist SlotMagie.
Und dann gibt es noch eine Handvoll erlesener Slot-Anbieter, die sich
von der Masse abheben und zu den deutschen Top Online Casinos gehören. Neuanmeldungen dürfen sich
über einen sehr guten Bonus mit Freispielen freuen. Mit RTP-Werten von bis zu 97% ist Wunderino aktuell außerdem auf dem deutschen Markt das Online Casino mit der höchsten Auszahlungsquote.
Abseits davon überzeugt das Casino natürlich
mit der deutschen Glücksspiel-Lizenz oder dem facettenreichen Portfolio an Spielen. Der Anbieter überzeugt im deutschen Vergleich mit dem stärksten Gesamtpaket, das für
jeden Spielertypen geeignet ist.
Ein effizienter und qualitativ hochwertiger Kundenservice ist ein wichtiges Kriterium bei der Bewertung
eines Online-Casinos mit deutscher Lizenz. Wir stellen sicher, dass das Casino verschiedene Kommunikationskanäle für
den Kundenservice anbietet, um den Bedürfnissen der
Spieler gerecht zu werden. Der Kundenservice ist ein wichtiger Aspekt
bei der Bewertung eines Online-Casinos mit deutscher Lizenz.
Der Bonus kann aus einem Prozentsatz der Einzahlung oder einem festen Betrag bestehen. Ein attraktiver Casino-Bonus kann ein wichtiger
Faktor bei der Wahl eines Online-Casinos mit deutscher Lizenz sein.
References:
https://online-spielhallen.de/bester-online-casino-bonus-2025-top-boni-in-deutschland/
Egal, ob Sie die Authentizität eines echten Casinos oder die Bequemlichkeit
des Online-Spiels suchen, Live-Casinos bieten das Beste aus beiden Welten. Live-Kasinos
bringen den Nervenkitzel eines echten Casinos direkt auf Ihren Bildschirm
und bieten ein interaktives Spielerlebnis, das seinesgleichen sucht.
Entdecken Sie das ultimative Online-Casino-Erlebnis für 2025
bei 24 Kasino, wo wir Ihnen nur das Beste aus der Welt der Online-Spiele bieten. Wir bieten alles vom neueste Online-Casinos voller neuer Spiele und innovativer Funktionen für das traditionsreichste Casinos
bekannt für Zuverlässigkeit und hohe Auszahlungen. LeoVegas bietet eine ausgezeichnete mobile App mit über 1.000 Slots und sehr schnellen Ladezeiten. Plattformen wie AskGamblers
oder Casino Guru führen sogenannte schwarze Listen mit bekannten Problemanbietern.
Vergewissern Sie sich, dass das Casino von einer seriösen Behörde
lizenziert ist. Spiele wie Blackjack, Roulette und
Baccarat sind in diesem Format sehr beliebt und bieten einen sozialen Aspekt, der bei traditionellen Online-Spielen oft fehlt.
Diese Spiele bieten ein realistisches Erlebnis,
das die Bequemlichkeit des Online-Spiels mit der Atmosphäre
eines landbasierten Casinos verbindet. Doch viele
Kasinos in Irland bieten außerdem responsive Websites,
die auf allen Browsern gut funktionieren und keine
Downloads erfordern. Dedizierte mobile Apps verbessern die Benutzerfreundlichkeit und bieten ein reibungsloses,
optimiertes Erlebnis. Außerdem bieten sie Anonymität, was für datenschutzbewusste Spieler attraktiv ist.
Top-Casinos bieten eine Mischung aus Kreditkarten, E-Wallets und
Banküberweisungen an.
References:
https://online-spielhallen.de/verde-casino-bonus-aktuelle-angebote-tipps/
Es gibt sehr viele Kriterien, die von unseren deutschen Casinoexperten bei der Bewertung eines neuen Online Casinos für das Spiel mit echtem
Geld angesetzt werden. Diese Online Spielhallen werden ausschließlich von deutschen Betreibern mit
einer gültigen Lizenz der Gemeinsamen Glücksspielbehörde der Länder (GGL) geführt.
Um dir eine vertrauensvolle Atmosphäre für Glücksspiele
bieten zu können, testen wir ständig Online Casinos auf Sicherheit, Datenschutz und seriöse Geschäftspraktiken. Auf unseriösen Casino Plattformen zu spielen, kann schwerwiegende Folgen haben, die weit
über den finanziellen Verlust hinausgehen. In den 70er und 80er Jahren kam das
Videopoker auf, mit dem du dieses Kartenspiel auch alleine spielen kann.
Blackjack kannst du auch im Live Casino deiner Online Spielbank spielen, wo du
in Echtzeit gegen einen echten Dealer dein Können beweisen kannst.
Ein lizenziertes deutsches Online Casino bietet
zudem sichere Zahlungsmethoden und Schutzmechanismen für verantwortungsvolles Spielen. Die beste Online Casinos Deutschland bieten dabei
nicht nur spannende Online Glücksspiele, sondern auch hohe Sicherheitsstandards und fairen Spielerschutz.
Dadurch gewährleistet ein reguliertes und seriöses Online
Casino Deutschland einen sicheren und verantwortungsbewussten Spielbetrieb
gemäß den deutschen Vorschriften. Dieser Prozess ist Teil der Voraussetzungen für den Erhalt einer deutschen Lizenz.
NV casino mobile ist an die Arbeit auf verschiedenen Geräten angepasst.
Die mobile Version und die App bieten vollen Zugriff auf das Spielgeschehen von jedem Gerät aus.
NV Casinos bietet bequeme Lösungen für Kunden. Status mit exklusiven Belohnungen bieten Anreize für Leistung
und Statusverbesserung. Für jede 5 €, die Sie ausgeben, erhalten Sie 1
Gratispunkt. Das Treueprogramm von NV Casino ermöglicht es Ihnen, Aktivitätsbonus zu verdienen.
NV Casino bietet seinen Spielern eine Vielzahl von sicheren und bequemen Zahlungsmethoden für
Ein- und Auszahlungen an. Spieler erhalten abhängig vom eigenen VIP-Level
zwischen 3 % und 12 % Rückzahlung auf ihre Nettoverluste.
Regelmäßige Spieler können jeden Freitag von einem Einzahlungsbonus von bis zu 700 € profitieren. Auch hier gilt eine maximale Gewinnbegrenzung
in Höhe des Fünffachen der Ersteinzahlung. Die Höhe des Bonus ist
abhängig von der Einzahlungssumme, der Umsatzfaktor beträgt 40x für Bonusgelder und
35x für Freispiele.
References:
https://online-spielhallen.de/beste-online-casinos-deutschland-top-10-nov-2025-3/
Wir raten dir auch davon ab, in Bitcoin Casinos
im Ausland zu spielen, falls du in Deutschland ansässig bist.
Ein Bitcoin Casino ist eine Seite mit Online Glücksspielen, die Bitcoin, eine Form
der Kryptowährung, für Transaktionen akzeptiert. Sie können spielen, ohne
persönliche Informationen preiszugeben. Es ist jedoch wichtig, nur bei
lizenzierten und vertrauenswürdigen Casinos zu spielen. Dank der breiten Unterstützung von Kryptowährungen und der Flexibilität der Plattform ist 22Bet
ideal für Spieler, die unkompliziert und anonym spielen möchten. Spieler
können aus einer Vielzahl an Slots, Tischspielen und Live-Casino-Titeln wählen. Winz.io
bietet eine beeindruckende Auswahl von über 5.000 Spielen, darunter Slots, Tischspiele und ein umfangreiches Live-Casino.
Ein solcher Krypto Casino Bonus ohne Einzahlung bietet Ihnen die Möglichkeit, das Online
Casino Krypto erst einmal kennenzulernen, bevor Sie
echtes Geld einzahlen. Unter den Bestandskundenangeboten finden Sie
oft auch Aktionen, bei denen Sie zwar eine Einzahlung leisten müssen, im Gegenzug aber
Freispiele erhalten. Auch bei einem Reload-Bonus kann es passieren,
dass das Crypto Casino Freispiele für einen oder mehrere Slots bereitstellt.
Dieser Bonus geht für gewöhnlich mit einer Mindesteinzahlung daher.
References:
https://online-spielhallen.de/top-9-online-casinos-in-deutschland-2025-serios-getestet/
Das NV Online Casino ist eine brandneue Glücksspielplattform, die erst im Jahr
2024 an den Start gegangen ist. Es bietet deutschen Spielern ein umfassendes Spielerlebnis.
Der Mindesteinzahlungsbetrag variiert je nach Bonusangebot – solche flexiblen Limits sind typisch
für Mindesteinzahlung Casinos. Hier werden verschiedene Einzahlungsmethoden unterstützt, darunter Bankkarten, Skrill, Neteller, Rapid
und Mifinity. Das Willkommenspaket umfasst
Boni auf die ersten drei Einzahlungen bis zu 2.000 € und 225 Freispiele.
Auf dieser Spieleplattform können Sie viele Spiele kostenlos ausprobieren. Auch Fans von Krypto Casinos kommen dank der breiten Spielauswahl auf
ihre Kosten.
200% bis zu 500€ + 200 Freispiele Höhere Stufen reduzieren die
benötigte Punktzahl pro Euro, was das Programm besonders
attraktiv für Vielspieler macht. Je mehr Sie spielen, desto höher steigen Sie in den Stufen auf – von Bronze über
Silber bis hin zu VIP-Platin. Nach der Registrierung und der ersten Einzahlung erhalten Sie einen Bonus,
der oft aus einer Kombination von Bonusgeld und Freispielen besteht.
Über hochauflösende Streams können Sie in Echtzeit mit professionellen Dealern interagieren, während Sie Spiele wie Blackjack, Baccarat
oder Poker spielen.
References:
https://online-spielhallen.de/top-crypto-slots-2025-spiele-wichtige-features/
Unser Live-Casino bietet eine breite Palette an Wetteinsätzen und abwechslungsreichen Live-Spielvarianten und ist so konzipiert, dass es sowohl Anfänger
als auch erfahrene Spieler anspricht. Das Live-Casino nutzt das Fachwissen erstklassiger Anbieter
von Live-Casino-Technologie und lässt die Spieler in eine breite Palette traditioneller Tischspiele
eintauchen, darunter Blackjack, Roulette, Baccarat und Poker.
Aus diesem Grund bieten wir eine Suchfunktion an, mit der die Spieler schnell
Spiele nach ihren Titeln finden können. Entfachen Sie Ihre Leidenschaft für das
Spielen im Hit’n’Spin Casino, wo unser riesiges Spieluniversum auf Sie wartet und ein unvergleichliches Erlebnis bietet,
das speziell auf unsere geschätzten Schweizer Spieler zugeschnitten ist.
Darüber hinaus sticht das innovative Buy Feature hervor, das den Spielern die Möglichkeit bietet, direkt
in Bonusrunden ausgewählter Spielautomaten einzusteigen, was sowohl den Nervenkitzel als auch die potenziellen Gewinne erhöht.
Für jede 10 CHF, die Sie bei unseren Spielen (ausgenommen Live Casino und Instant Games) einsetzen, erhalten Sie einen Gratispunkt.
Ihr Status in unserem Loyalitätsprogramm hat direkten Einfluss auf den wöchentlichen Bonusbetrag, den Sie erhalten können.
Besonders beliebt sind die Wochenendturniere mit erhöhten Gewinnsummen und zusätzlichen Freispielen als Belohnung für die besten Teilnehmer.
Sie können unbegrenzt im Übungsmodus spielen und erst dann auf Echtgeld umsteigen, wenn Sie sich
vollkommen sicher fühlen. Die intuitive Benutzeroberfläche ermöglicht Ihnen, mühelos zwischen den verschiedenen Slots und Tischspielen zu wechseln. Wager x40 (Geldbonus)
x30 (Freispiele)
References:
https://online-spielhallen.de/hitnspin-casino-test-bonus-spiele/
Diesen kannst du oftmals zusammen mit weiteren Einzahlungsboni nutzen. In einigen Fällen stellt der Online
Casino Registrierungsbonus ohne Einzahlung einen Teil
eines Willkommenspakets dar. Hierzu gehören nicht nur die Umsatzanforderungen der Bonusgelder,
sondern auch möglicher Freispiel-Gewinne. Gewertet werden jedoch nicht nur deine persönlichen Einzahlungen, sondern auch
die in den Spielen erzielten Zwischengewinne.
1️⃣ Wählen Sie ein Bonusangebot ohne Einzahlung aus,
das Sie erhalten möchten. In einigen Fällen ist ein exklusiver Promo-Code
erforderlich, um den Bonus ohne Einzahlung zu erhalten. Nach der
Anmeldung wird das Gratis-Spielguthaben oder die Freispiele automatisch Ihrem Konto gutgeschrieben. Um den beworbenen Bonus ohne
Einzahlung zu erhalten, müssen Sie lediglich ein Konto bei
einem Casino Ihrer Wahl erstellen. Auf dieser Seite finden Sie eine Vielzahl
von Casinos mit Bonus ohne Einzahlung, die Ihnen gratis
Guthaben oder Freispiele anbieten. Am Ende dieser Seite finden Sie außerdem
einen Stream mit den neuesten Bonusangeboten.
Normalerweise erhältst Du ein paar Spins kostenlos und in einigen Fällen sogar
echtes Geld, um nach der Registrierung zu spielen. Viele Casinos bieten neuen Spielern die Möglichkeit, einen Echtgeld Bonus auf dem Handy zu erhalten, ohne dass
zuvor eine Einzahlung nötig ist. Ein Bonus ohne Einzahlung ist besonders attraktiv für
mobile Nutzer, die gerne unterwegs spielen.
References:
https://online-spielhallen.de/vegas-casino-bonuscode-ihr-schlussel-zu-aufregenden-belohnungen/
What makes 999,999,999,999,999,999,999 an interesting number from
a mathematical point of view? Just find the currency and get spelling for it.
By using this site you accept our terms and conditions including our
privacy and cookie, copyright and permissions policies.
Every whole number greater than 1 is formed from at least one prime factor.
Below you’ll find its key properties, along with some statistical info, fun facts and trivia.
Discover the secrets of 999,999,999,999,999,999,999 with our full breakdown of its prime factors, divisors, and mathematical properties…
This visualization shows the relative proportions of its 7 prime factors
(outer circle), plus the relationship between these
and its 256 divisors. You could say that a number is made
or ‘composed’ of its prime factors. Its factors, divisors, and base properties can show some interesting behavior.
References:
https://blackcoin.co/clams-casino-in-depth-review/
All payment methods boast instant processing times and
no hidden fees, making transactions straightforward and hassle-free.
With themed “shots” and promo codes, this lounge experience adds flavour and
creativity to the bonus calendar. Complete
specific challenges, and you’ll earn additional Free
Spins to enjoy on-top games.
Interact with professional, friendly dealers in real-time as you play your favourite table games.
From the classic reels to the most innovative new releases,
our universe of casino games is designed to satisfy every player’s desire.
Players can expect to see new titles added to the online pokies library, as well as new sports betting
markets and live casino games.
References:
https://blackcoin.co/casino-jax-in-depth-review/
online poker real money paypal
References:
https://sportsprojobs.net/employer/142928/paypal-casinos-2025-paypal-casino/
online casino uk paypal
References:
corerecruitingroup.com
The “Boomerang” cashback bonus at Ozwin acts as a safety net when luck isn’t on your side. Be sure to watch out for these bonus codes each time you log in for a potentially rewarding surprise! A thrilling aspect of the Ozwin Casino experience is the Ozwin Casino No Deposit Bonus. Create your own winning story at Ozwin Casino, where bonus-driven fun never ends. Enjoy a one-of-a-kind experience filled with rewards every step of the way as you explore the Ozwin Casino lobby.
The team helps with transaction issues and ensures a smooth experience. Oz casino ensures fair and transparent transactions. Some methods may take longer to reflect in the account. The casino processes requests within 24 to 48 hours.
References:
https://blackcoin.co/ufo9-casino-your-place-to-play-your-way/
online american casinos that accept paypal
References:
assamwork.com
casino sites that accept paypal
References:
carecall.co.kr
casino sites that accept paypal
References:
https://recrutement.fanavenue.com/companies/payid-online-casinos-in-australia-for-2025-play-payid-pokies/
casinos paypal
References:
https://exelentsmart.com/employer/best-australian-casino-sites-2025-aussie-online-casinos/
Krypto Casinos bieten eine große Auswahl an Bonusangeboten, die oft großzügiger ausfallen als in traditionellen Fiat Online Casinos. Zudem bieten viele dieser Casinos das sogenannte Provably Fair Gaming, bei dem die Fairness der Spiele eigenständig überprüfbar ist. Zusammen mit der großen Spielauswahl, bei der uns vor allem das Live Casino nachhaltig beeindrucken konnte, gibt CoinCasino eine top Empfehlung ab. Liegt eine deutsche Lizenz vor, gelten verschiedene Einschränkungen bei Einzahlungen, Einsätzen und Spielauswahl. Krypto Casinos ähneln traditionellen Online Casinos in vielen Punkten, allerdings schneiden sie bei Anonymität, Bonus, Spielauswahl und Sicherheit überwiegend besser ab.
Beide Casinoformen bieten Unterhaltung auf hohem Niveau, unterscheiden sich jedoch in einigen zentralen Punkten wie Zahlungsmethoden, Anonymität, Geschwindigkeit und Regulierung. Tatsächlich bieten viele Plattformen besonders attraktive Bonusaktionen, um neue Spieler anzulocken und bestehende Nutzer langfristig zu binden. Ein gutes Krypto-Casino sollte eine gesunde Mischung aus bekannten Anbietern und exklusiven Eigenproduktionen bieten. Diese sogenannten „Originals“ sind meist einfach gehalten, bieten transparente Gewinnchancen und sind besonders bei Krypto-Enthusiasten beliebt – zum Beispiel Dice, Crash oder Plinko.
References:
https://onlinegamblingcasino.s3.amazonaws.com/goodwin%20casino.html
Handverlesen, die eine perfekte Kombination aus Sicherheit, aufregendem Gameplay und großzügigen Boni mit schnellen und zuverlässigen Zahlungsanbietern bieten. Darüber hinaus musst du keine Anreise auf dich nehmen und kannst flexibel und anonym von Zuhause aus spielen. Besonders attraktiv sind zudem Anbieter, die neben dem Willkommensbonus auch Aktionen für Bestandskunden wie Treueprogramme anbieten.
Ein attraktiver Casino-Bonus kann ein wichtiger Faktor bei der Wahl eines Online-Casinos mit deutscher Lizenz sein. Der Casino-Bonus ist ein wichtiger Aspekt bei der Bewertung eines Online-Casinos mit deutscher Lizenz. Diese verschiedenen Möglichkeiten bieten den Spielern eine breite Palette an Optionen und Spielstilen, um ihre individuellen Vorlieben und Gewinnziele zu erfüllen. Casino-Rubbellose bieten eine schnelle und einfache Spieloption mit sofortigen Gewinnmöglichkeiten.
References:
https://s3.amazonaws.com/onlinegamblingcasino/best%20casino.html
In den höheren Levels erhältst Du jede Woche einen wöchentlichen Einzahlungsbonus mit Bonusguthaben und Freispiele, zudem steigt der persönliche Cashback Prozentsatz an. Die zu diesem Bonus gehörenden Umsatzbedingungen sind relativ fair, denn Du musst das Bonusgeld nur 40 Mal umsetzen, ehe eine Auszahlung möglich ist, die Gewinne aus den Freispielen sogar nur 30 Mal. Einzahlen, Geld leer spielen, das war’s. Macht spaß dort zu spielen. Gute spile aber lass mich mit dise bewerten kann ich nicht spielen Stört mich! Ein Design und Stil volles online Casino schnelle Auszahlungen einen gute und schnell erreichbaren Kundenservice für alle Angelegenheiten in einem live Chat verpackt.
Diese Spiele nutzen die RNG (Random Number Generator) Technologie, um nachweislich faire Spiele und unvoreingenommene Ergebnisse zu gewährleisten. Der Spielautomatenbereich im NV Casino ist besonders beeindruckend und bietet eine große Auswahl an Titeln für jeden Geschmack. Die Plattform bietet eine Vielzahl von sicheren Zahlungsmethoden, die für deutsche Spieler geeignet sind und schnelle Auszahlungen und sichere Zahlungen gewährleisten. Ja, NV Casino ist für Spieler in Deutschland zugänglich und bietet eine lokalisierte Erfahrung mit Unterstützung für die deutsche Sprache und akzeptierte Währungen einschließlich des Euro.
References:
https://s3.amazonaws.com/new-casino/verde%20casino%20bonus%20ohne%20einzahlung.html
References:
Anavar woman before after
References:
https://firsturl.de/VnWVQ0F
References:
Choctaw casino pocola ok
References:
https://dreevoo.com/profile.php?pid=944783
References:
Play online blackjack
References:
https://bookmarkfeeds.stream/story.php?title=aussie-dollar-casino-payments
References:
Comanche red river casino
References:
https://platform.joinus4health.eu/forums/users/latexhammer2/
medical usage of steroids
References:
https://www.mapleprimes.com/users/queenkey5
female cutting cycle steroids
References:
https://freebookmarkstore.win/story.php?title=top7-suplementos-para-aumentar-la-testosterona-vitaminas-y-pastillas-que-debes-conocer-somos-madrid
References:
Girls before and after anavar
References:
https://lovewiki.faith/wiki/Anavar_Erfahrungen_Zyklus_Anavar_Frauen_Steroid_2026
References:
Anavar female before and after reddit
References:
https://md.swk-web.com/s/15wCR44DUa
best legal steroid alternatives
References:
https://socialbookmarknew.win/story.php?title=buy-winstrol-depot-injectable-usa-domestic-and-worldwide
best oral steroids for beginners
References:
https://lovewiki.faith/wiki/Dianabol_Methandienone_Acheter_au_Meilleur_Prix_en_France
d anabolic steroids
References:
https://hack.allmende.io/s/bCzfcFCMC
References:
Anavar before after meal
References:
https://sargent-demant.technetbloggers.de/anavar-oxandrolone-guida-per-gli-utilizzatori-dei-cicli-di-steroidi
References:
Take anavar before or after workout
References:
https://hussein-noer-2.hubstack.net/anavar-vorher-nachher-die-guten-und-schlechten-wirkungen-von-oxandrolon
effects of steroids on females
References:
https://lovewiki.faith/wiki/Acquista_online_in_Italia_senza_ricetta
References:
Club regent casino
References:
https://www.garagesale.es/author/maskfish77/
References:
Casino ru
References:
https://may22.ru/user/wirenode46/
References:
Lucky star casino concho
References:
https://bookmarkfeeds.stream/story.php?title=candy-kontaktformular-fuer-alle-informationen
References:
Platinum play
References:
https://pad.geolab.space/s/dXN5VkeQ2
References:
Casino online
References:
https://humanlove.stream/wiki/Candy_Crush_Jeux_en_ligne_6jeux_fr
References:
Royal vegas mobile casino
References:
https://brewer-wang.federatedjournals.com/claim-your-bonus
References:
Casino grand luxe
References:
https://gratisafhalen.be/author/lyriclove09/
References:
Boulevard casino
References:
https://justbookmark.win/story.php?title=pardon-our-interruption
References:
Las vegas casino budapest
References:
https://500px.com/p/vinterwbjknudsen
References:
Avalon casino
References:
http://ezproxy.cityu.edu.hk/login?url=https://candy96.eu.com/fr-fr/
References:
Casino hull
References:
https://fakenews.win/wiki/Candy_Casino_Review_2026_Slots_Bonuses_Ratings
References:
Aristocrat slot machines
References:
https://sciencewiki.science/wiki/Candy96_Casino_Australia_Pokies_Bonus_Deals_Fast_Withdrawals
difference between anabolic steroids and testosterone
References:
https://bookmarkspot.win/story.php?title=clembuterol-landerlan-50-capsulas
%random_anchor_text%
References:
https://hikvisiondb.webcam/wiki/CIMA_PROSPECTO_TESTAVAN_20_MG_G_GEL_TRANSDERMICO
best natural anabolics
References:
https://yogaasanas.science/wiki/Acheter_Dianabol_sur_Internet_DianabolSteroids_com
%random_anchor_text%
References:
https://postheaven.net/troutboard39/beste-appetitzugler-die-16-besten-produkte-im-vergleich
%random_anchor_text%
References:
https://commuwiki.com/members/crowdwire6/activity/17252/
muscle growing pills
References:
https://linkvault.win/story.php?title=anabolic-steroid-induced-gynecomastia-causes-and-effective-treatments
steroid before and after first cycle
References:
https://pads.jeito.nl/s/WUtIEiVRcp
why steroids should be legal in sports
References:
https://lovewiki.faith/wiki/Testosterone_Boosters_How_to_Boost_Testosterone_Naturally_Over_50
anabolic steroids for sale usa
References:
https://ekademya.com/members/jefftaste53/activity/174895/
anabolic steroids high blood pressure
References:
https://scientific-programs.science/wiki/What_Drugs_Will_Make_You_Lose_Weight_Effective_Safe_Proven
what’s the biggest you can get without steroids
References:
https://hack.allmende.io/s/KyCiOjDrH
what supplements have steroids in them
References:
https://bom.so/cQlc8i
References:
Slots belgique
References:
https://pattern-wiki.win/wiki/Claim_Your_Bonus
References:
Monkey money
References:
http://lideritv.ge/user/clothcrayon0/
References:
Play online casino games
References:
https://sciencewiki.science/wiki/96_com_1_Trusted_Online_Casino_Sports_and_Crypto_Betting_Site
References:
Paradise casino
References:
https://cameradb.review/wiki/Play_the_Best_Online_Casino_Games_at_Candy96_Pokies_Table_Live
References:
Ladbrokes slots
References:
https://menwiki.men/wiki/Candy96_Reviews
References:
Pink floyd eclipse
References:
https://pad.karuka.tech/s/HAgOfcYcn
References:
Pink floyd live at pompeii
References:
https://botdb.win/wiki/Top_Real_Money_Online_Casino_2026
References:
Hardrock casino hollywood fl
References:
https://writeablog.net/templeafrica18/official-site-in-united-kingdom-2025
References:
Little river casino
References:
https://cameradb.review/wiki/Online_Casino_De_Beste_Online_Casinos_van_Nederland_voor_2025
References:
Manoir richelieu charlevoix
References:
https://pad.stuve.de/s/_Xc02fBYf
bad reaction to steroids
References:
http://historydb.date/index.php?title=vestpost5017
mass gaining steroids
References:
https://diego-maradona.com.az/user/koreandrain9/
alpha mass stack
References:
https://bookmarkzones.trade/story.php?title=amazon-com-nugenix-total-t-suplemento-potenciador-de-testosterona-libre-y-total-para-hombres-90-unidades-
steroid cycle chart
References:
https://pailpoland7.bravejournal.net/objetos-que-denotan-niveles-de-testosterona-bajisimos
References:
Casino express
References:
https://pad.karuka.tech/s/0vPtzDmXf
References:
Thief river falls casino
References:
https://pattern-wiki.win/wiki/Casino_Bonus_ohne_Einzahlung_und_Codes_Januar_2026
References:
Crown casino melbourne accommodation
References:
https://www.youtube.com/redirect?q=https://online-spielhallen.de/1red-casino-deutschland-eine-tiefenanalyse-fur-spieler/
References:
Campione d italia casino
References:
https://kanban.xsitepool.tu-freiberg.de/s/BJUZsyi8Zg
References:
Arkansas casinos
References:
https://lykkegaard-goodman.mdwrite.net/online-casino-auszahlung-2026-ratgeber-schnelle-auszahlung
References:
Great canadian casino
References:
https://trade-britanica.trade/wiki/PayID_Casinos_In_Australia_Secure_Instant_Casino_Payments
References:
Aspers casino milton keynes
References:
https://telegra.ph/Winz-Casino-Play-Online-Casino-With-Zero-Wagering-02-02
References:
Jacks or better video poker
References:
https://hedge.fachschaft.informatik.uni-kl.de/s/imLQ-5Uf5
References:
Boogie nights hollywood casino
References:
https://sciencewiki.science/wiki/PayID_Online_Casinos_Australia_Instant_Withdrawals_2026
winstrol prices
References:
https://skitterphoto.com/photographers/2214727/cooper-oneil
how long does it take to get over steroid withdrawal?
References:
https://dreevoo.com/profile.php?pid=1054191
anabolic steroids description
References:
https://coolpot.stream/story.php?title=hautpflege-produkte
References:
Casino jackpots
References:
http://volleypedia.org/index.php?qa=user&qa_1=fogstove12
best muscle gain products
References:
https://hester-tolstrup-2.thoughtlanes.net/dbol-50mg-tablets-for-muscle-gain
negative side
References:
https://cameradb.review/wiki/How_to_Safely_Order_Anavar_Online_A_Complete_Guide_for_2025
lean steroid cycle
References:
https://clashofcryptos.trade/wiki/Dianabol_Prohormone_HiTech_Pharmaceuticals
I was studying some of your blog posts on this site and I think this web site is very informative! Continue putting up.
is larry wheels on steroids
References:
https://firsturl.de/wzF3e8j
anavar steroid for sale
References:
https://socialisted.org/market/index.php?page=user&action=pub_profile&id=314789
gnc fitness app
References:
http://jobs.emiogp.com/author/flagsilk0/